You know by now that eating too many carbohydrates and sugars makes you fat and are genuinely not too good for you, but are they really that bad? And do you have to totally eliminate them from your diet?

Why do carbohydrates have a bad rep?
Consuming too much carbohydrates and sugar is the main reason why we become fat and overweight. Obviously ‘Calories out V calories in’ has a role to play, but the main reason we get fat is excess carbohydrate and sugar consumption, not excess calorie consumption.
I also believe that processed sugars and carbohydrate is the main culprit for most of our modern-day health problems including, obesity, type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
However this doesn’t necessarily mean we have to go from one extreme to another. You don’t have to choose between a zero carb and a low-fat diet approach. A lot of people are terrified of eating sugar and carbohydrate, but eating sugars and carbohydrates at certain times can actually help you with things such as replenishment after training, recovery, building muscle and the production of hormones
On the other hand though our bodies run perfectly well without carbohydrates. They are not essential like some fatty acids (fat) and amino acids (protein). Our bodies function perfectly well on just fat and protein.
So why does carbohydrate make you fat?
Like I have said in other posts and articles: all sugars are carbohydrates. Obviously some carbohydrates are more complex and harder to digest than others, but the majority of them all end up causing the same thing – an insulin response.
Regardless of whether it’s ‘low in fat’ or ‘whole grain’ it’s going to cause an insulin response, which in turn triggers fat storage and stops fat burning.
This is something you certainly don’t want.
Most people would eat 3-5 meals a day all containing some type of sugar or carbohydrate. Over a day that’s a lot of insulin, causing a lot of fat storage and stopping fat metabolisation. Over time this causes you to get fat and eventually insulin stops working for you.
This is called insulin resistance or diabetes.
When we eat cereal, bread or sugar in general our body breaks it down in to blood sugar (glucose). This will cause a problem for our bodies, as it needs a stable blood sugar level. Our body will respond to this sudden spike of blood sugar our bodies will release insulin. Insulin’s job is to take this blood sugar and put it somewhere useful.
There are 3 places this blood sugar goes:
Liver glycogen (liver blood sugar stores) – depletes after aerobic & jogging exercise.
Muscle glycogen (muscle sugar stores) – depletes after resistance training, aerobic exercise and high intensity training (HITT).
Adipose tissue (body fat) – stores when sitting in work, even if you have an active job and generally doing nothing.
You can have some influence to where this blood sugar goes. If you consistently lift heavy shit (barbels and Dumbbells) or perform some type of resistance training then muscle glycogen replenishment will soon become the main priority as it’s constantly being depleted and needs restoring.
If you have low liver glycogen levels from, jogging, fasting or not eating – this will be topped up. The downside is that the liver will only hold around 400 calories of glycogen (blood sugar) so very often this fills up and spills over. This results in this extra blood sugar/ glycogen going to one of the other two places – adipose tissue (body fat/spare tyre) or muscle glycogen.
Last, but not least, if you sit around all day and do nothing chances are it will end up as adipose tissue (body fat). Over time this will build up (get fatter) and before you know it you’re overweight.
Who should eat carbohydrates and who shouldn’t?
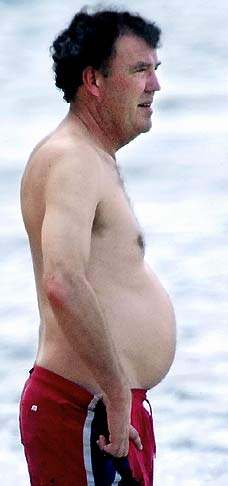
Person A – Overweight, pre diabetic, diabetic, little pot belly, wants to drop fat
If you match the above profile then I suggest limiting your carbohydrate to a maximum of two carby meals per week (not including green veggies).
When you achieve a decent body fat level you can introduce more carbohydrates back in to your diet especially if you’re performing regular resistance training.
By replacing carbohydrates with more protein and fat you will control your blood sugar levels better. In the long-term this will lower your chances of heart disease, help you lose body fat improve your cholesterol profile, and help control diabetes.
Person B – Wants to build muscle, skinny, performs resistance training, athlete
If you’re one of the above then you can get away with eating more carbohydrates and sugars. Athletes, skinny people and “hard gainers” can eat high amounts of carbohydrates and not have any problems with storing excess body fat. They genuinely need them to help recover from training and build muscle tissue.
If you’re just an average gym rat, looking to stay lean and add small amounts of muscle whilst minimising body fat storage, carbohydrate meals post training would be my personal recommendation.
You can then eat MOAR amounts of protein and fat on the days you’re not lifting iron or performing some type of interval or sprint work.
Your main carbohydrate sources should come from foods such as sweet potato, white rice, berries, nuts and green vegetables. Always try to some type of protein source with your carbohydrate meals.
For the athletes and hard gainers, white vegetables such as parsnips, turnips and potato are fine. Carbohydrates you genuinely want to avoid are wheat based foods such as pasta, bread (whole grain as well), spaghetti, cereal, milk, fruit juices, chocolate, sweets and cake.
Jay Farrant – Personal Trainer Dublin.
